
- NATIONAL GEOSPATIAL-INTELLIGENCE AGENCY

Part I: Analyzing China's Continued Expansion of Coal-Fired Power Capacity
In September 2020, against the backdrop of the coronavirus pandemic and with the global economy still reeling, China pledged that it would achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. In this two-part series, researchers from the Columbia School of International and Public Affairs explore China's progress towards that goal along two vectors: "brown" and "green". Part I ("brown") identifies 5 coal-fired power plants, approved in March 2020, and tracks their construction and continued development.
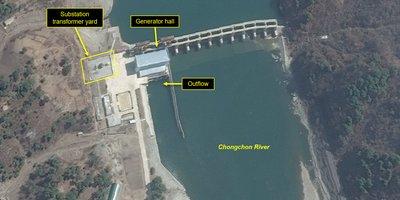
North Korea's Hydroelectric Power – Part I
North Korea has faced persistent challenges in generating sufficient electricity to meet its industrial and civil needs. While coal is a primary source of energy consumption, hydroelectric power is the predominant method of electricity production.

A Snapshot of North Korea's Supply Chain Coal Activity – Part II
Based on an initial look at North Korea's coal industry, the country's larger coal mines have remained active despite the increasing restrictions on the North's coal exports.

A Snapshot of North Korea's Supply Chain Coal Activity
Despite increasing restrictions on the DPRK's coal exports, the country's larger coal mines have remained active from 2015 to 2019 and improvements have been made to its coal supply-chain infrastructure.

Part 2: Ore Car Activity Up at Wonsan Railway Rolling Stock Complex
Update on North Korea's largest railroad rolling stock manufacturing and repair facility.