
- NATIONAL GEOSPATIAL-INTELLIGENCE AGENCY
Quantifying Increases in Maritime Activity in Information-Denied Environments Using Open-Source SAR Data
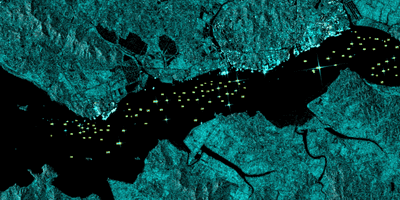
The application of a basic geographic information system (GIS) workflow and cloud-based processing of publicly available Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images, within a Google Earth Engine environment, demonstrates the ability to track large maritime vessel activity patterns on the Taedong River proximal to Nampo Port in Nampo, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK) with a high degree of accuracy. This maritime vessel activity was observed over a period of 10 years (2015-2025). The automated methodology utilized to analyze this activity has no statistically significant bias (95% CI -0.22 – 0.45) with a mean absolute error of 0.81 ships per image across the entire area of interest.
Analysis identified multiple temporal points of interest where there were significant changes in maritime activity, providing quantitative context for further in-depth qualitative research. The automated methodology described can be replicated on other ports or narrow maritime areas of interest to generate contextual quantitative data on large vessel movements and activity over long time periods.